Dental Caries (Teeth Cavities) Cause Toothache and Jaw Pain
Dental caries (tooth/teeth cavities) afflicts most of us at some point in life and is the second most common condition in humans after the common cold and flu. If left untreated it can progress to the point where it results in unbearable pain. Depending on the extent of the damage to the tooth, the tooth may have to be removed (extracted) by a dental professional.
What is a tooth cavity?
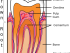
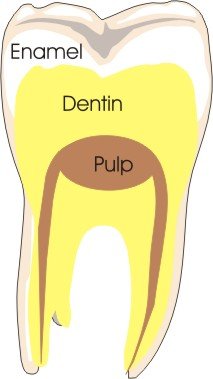
A tooth cavity is the gradual breakdown of the tooth structure due to microbial growth. Erosion of the outer lining of the tooth (enamel) is followed by the destruction of the inner layer (dentin). It can occur with a crack in the enamel that is left untreated but poor dental hygiene is one of the main causes.
How do cavities form in the tooth?
A tooth cavity occurs as a result of a combination of factors.
- Food particles get trapped on and between the teeth after eating.
- Along with mucus, dead epithelial cells (from the mouth lining) and bacteria, a thin soft film, known as plaque coats the teeth.
- This provides the ideal medium for oral bacteria to feed upon food debris.
- Bacteria like Mutans streptococci and related groups, break down food particles and produce lactic acid as a byproduct. It is this lactic acid that is responsible for eroding tooth enamel and causing tooth cavities.
Food + Mucus + Dead Cells + Bacteria = Soft Plaque (within 24 hours after brushing)
Soft Plaque + Calcium +Phosphates + Other Compounds = Hard Plaque (within 72 hours of soft plaque formation)
Left untreated, the lactic acid will continue to erode the enamel and dentin and cause irritation of the nerve which is experienced as a toothache.
Pain with a Tooth Cavity
A toothache (painful and tender tooth) is a late symptom of an untreated tooth cavity. Toothaches may also be caused by an infection, injury or the absence of a tooth.
Jaw pain may also occur as a result of a dental cavity as the nerve supply of a tooth follows a path around or near the jaw. However, jaw pain should not always be mistaken for a dental cavity as there can be other causes like TMJ dysfunction (temporomandibular joint syndrome), or more serious causes like angina or a myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Jaw pain may precede, be accompanied by or follow after a toothache and this jaw pain may often radiate around the side of the affected tooth. This jaw pain can vary from dull pain in the early stages to severe throbbing pain with tenderness around the affected tooth.
Causes of Tooth Cavities
The risk factors below will often promote bacterial growth thereby causing a tooth cavity.
- Poor dental hygiene
- Low fluoride exposure
- Acidic foods and drinks
- Defects of the tooth (natural or inflicted)
- Reduced saliva production
- Recession of the gums
- Excessive dental fillings – fractured or weakened fillings may allow for bacterial infiltration.
- Pregnancy – excessive intake of refined carbohydrates in pregnant women.
Symptoms of a Tooth Cavity
Symptoms may vary depending on the location and severity of the cavity.
- Toothache (late symptom)
- Dark spots on tooth at the site of the cavity
- Tenderness upon pressure, eating, cold or warm drinks, air entering through mouth breathing
- Halitosis (foul smelling breath)
- Jaw pain
- Earache
- Swelling of the affected side
- Bleeding
Diagnosis
Diagnosis can be made simply by a using a dental probe to detect sensitivity at affected areas. A dental X-ray will provide further information on the severity of the cavity as well as any other considerations before commencing treatment. Please consult with a dental practitioner to confirm diagnosis of a tooth cavity.
Treatment
Treatment is dependent on the severity of the cavity. Destroyed tooth structure cannot be regenerated and has to be removed. The area is filled with a restorative composite material (filling) and in severe cases, removal of the affected tooth may be necessary (extraction).
Treatment of a dental cavity should not only be undertaken once there is a toothache or jaw pain. Immediate dental attention should be sought if any sign of a tooth cavity is evident. A common practice of using home remedies to treat a toothache like alcohol spirits and ice or the use of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) will only offer short term relief.
Management
After the appropriate treatment, simple lifestyle and dietary changes coupled with a strict dental hygiene program can ensure that future tooth cavities are minimized. The following should be considered :
- Daily use of fluoride in a suitable toothpaste when brushing, preferably twice daily.
- Brushing with a suitable toothbrush to physically remove plaque build up. Once hard plaque forms, it is difficult to remove with a toothbrush and therefore daily brushing is essential.
- Reduce intake of acidic foods and drinks and those high in refined carbohydrates (especially sugar).
- Regular consultations with your dentist is essential to maintain dental health.
Complications of Untreated Tooth Cavities
Untreated dental caries will often complicate without immediate dental attention. Erosion of both the enamel and dentin will finally affect the pulp of the tooth, the area containing the tooth’s blood vessels and nerves. If the remaining tooth structure can be preserved, a ‘root canal‘ (endodontic therapy) may be considered to prevent bleeding and stop the pain.
Severe damage of a tooth and removal of the destroyed tooth structure impacts on the cosmetic appearance of the teeth or impairs a normal bite. In these cases a crown may be used on the remaining tooth. In the cases of an extraction or loss of a tooth, the use of a bridge may be warranted.
Untreated tooth cavities can result in a dental abscess of the surrounding structures, gums, cheek, throat or under the tongue. In severe cases, the infection can spread to the mandible (lower jaw bone) or maxilla (upper jaw bone). A dental abscess requires incision and drainage with a prescription of antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drugs after the procedure.
Dental surgery and restoration procedures can be time consuming and costly. It is important to note that leaving a simple tooth cavity unattended can result in complications or require dental procedures that may not be covered by your dental plan. Proper dental hygiene and regular visits to your dentist (at least twice a year) can save you considerable inconvenience and discomfort.