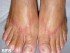
Itchy Arms and Hands – Causes and Treatment
Keratosis Pilaris (Chicken Skin)
Keratosis pilaris is a benign skin condition with small bumps (goose bumps, chicken skin) appearing on the upper arms or other parts of the body (1). Sheded skin cells, instead of falling off, build up in the hair follicles and plug them, thus causing skin bumps. Condition is hereditary and pretty common. It may appear in babies, usually becomes apparent in adolescents, and tends to cease with age. It may be associated with a dry skin, ingrown hair, or rarely, atopic dermatitis.
Symptoms:
- Small, hard, skin-colored, red, or brown bumps on the outer and back side of the upper arms (Picture 1), thighs, cheeks, upper back, or other parts of the body, giving a chicken skin or goose bumps appearance
- Bumps may (rarely) itch
- Bumps get bigger in cold weather and may clear up in summer
- Several types of keratosis pilaris, occurring on the eyebrows, scalp, or other body parts exist (1)
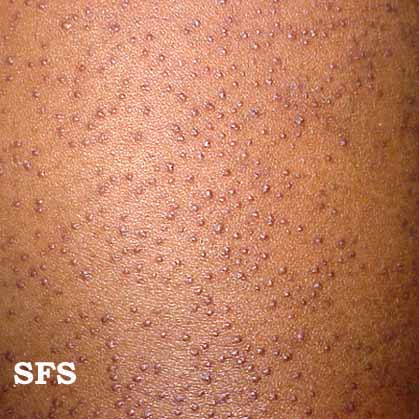
Picture 1. Thickened hair follicles in keratosis pilaris.
(source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D., atlasdermatologico)
Avaliable treatment (will not cure the condition completely) (2):
- Moisturizing creams containing urea, salicylic or lactic acid, or tretionine
- Rubbing with a pumice stone in a shower
- Exfoliants (ointments that cause skin peeling) like retinoids (should be not used in pregnancy and in babies)
- Laser assisted hair removal
- Acne removal with a needle, chemical peels, microdermabrasion, blue-light, laser, and intense pulsed light devices
Treatment has to be continuous, since skin thickening in keratosis pilaris is a continuous process.
“Upper Arm Acne”
Red bumps with occasional white centers, that may appear on the shoulders and upper arms (but also on the face, back, buttocks and thighs) may be:
- Common acne. Acne vulgaris on the upper arms may appear not only in adolescents but also in adults
- Staphylococcal folliculitis
- Hot tub folliculitis
- Herpes zoster (shingles)
Brachioradial Pruritis (BRP) – Itchy Upper Arm Syndrome
Brachioradial pruritus (once called itchy upper arm syndrome) is an intense itch appearing on the back and outer parts of the arm (1). The exact cause is not known, but a damage of the nerves in the sun exposed skin was observed. Age related deformations of bonny tissue in the neck spine that compress on nerves supplying the arm can be sometimes found. The disorder has not been found in individuals below 18 years of age so far.
Symptoms (4,5):
- Itchy, burning or tingling sensation on the sun exposed parts of the upper arm, forearm or/and shoulders (but not on other parts of the body). One or both arms may be affected.
- Itch is especially prominent at night
- No rash is usually present
- Symptoms correlate with direct sun exposure and often disappears in winter
- Symptoms may last from several weeks to several years
Diagnosis. Skin biopsy, where a small part of skin is examined under the microscope, may show damaged skin nerves and reduced skin tissue (skin atrophy).
Treatment options (3):
- Ice cubs or cold wet clothes placed over an affected area almost always helps
- Topical capsaicin may provide temporary relief
- Antihistamines or tricyclic antidepressants by mouth may help you to sleep
- Chiropractor may help you, if you have a spine related disorder
- Acupuncture was shown to be effective in some cases
Prevention is in wearing long-sleeved shirts, avoiding sun between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., using sunscreens and avoiding scratching.
Pompholyx
Pompholyx (vesicular or dyshidrotic eczema) is a common type of a skin inflammation with blisters, affecting the hands and/or feet. The exact cause is not known; pompholyx is often connected with sweaty palms (palmar hyperhidrosis), though.
Symptoms:
- Wet blisters, dry red bumps, swollen skin around the nails or cracks may appear on the hands, fingers and sometimes on the feet or toes
- Prominent itching
Symptoms are aggravated by irritant substances, like detergents or solvents.
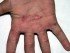
Picture 2. Pompholyx, dyshidrotic eczema on the palm.
(source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D., atlasdermatologico)
Treatment is rarely completely effective:
- To dry up the blisters, apply Burrow’s solution (aluminium acetate), or 1% vinegar for 15 minutes four times a day
- In dry skin, moisturizing cremes should be used
- In an intense inflammation, short term (up to 14 days) corticosteroids (as moisturizer, or taken by mouth) are effective, but condition may reoccur shortly after stopping treatment
- If a staph skin infection appears, it should be treated with appropriate antibiotics
- PUVA therapy with ultraviolet light usually helps
Hand Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis may be triggered by prolonged exposure to irritant substances such as detergents, solvents, or car oil.
Allergic dermatitis may occur 48-72 hours after exposure to substances that can cause allergy: PPD in hair dyes, rubber accelerators in gloves, nickel in jewelry and metal closures on cloth, chromates in shoe leather, antibiotic neomycin, fragrance, lanolin in ointments and cosmetics, formaldehyde, psoriasis, and genetic factors.
Symptoms:
- Red and dry skin on the back or palm side of the hands that can progress to itchy bumps, vesicles, scaling, cracking, weeping or swelling, that may last for several weeks/months or until irritation does not stop
- Hives, a swollen red patch of skin, may appear in allergies and last about 20 minutes
Diagnosis. Patch skin tests can be performed to distinguish between a contact and allergic dermatitis.
Treatment. In prolonged allergy, antihistamines by mouth can be taken. Severe inflammation can be treated with corticosteroids.
Prevention is in avoiding wet work and irritant substances, using gloves (vinyl gloves ca be used, if you have an allergy to rubber gloves), and moisturizing cremes.
Palmoplantar Keratoderma
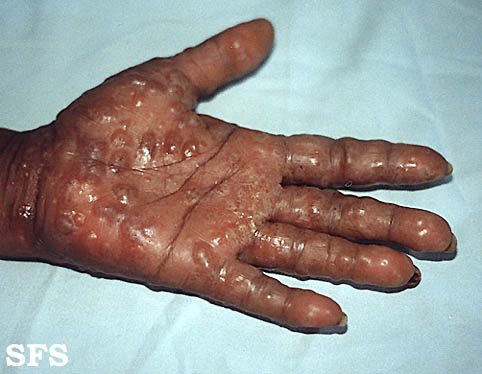
Palmoplantar keratoderma means marked thickening of the skin on palms and/or soles (Picture 3). A thickened skin may itch or not. Condition may be inherited or related to eczema, psoriasis, infections, medications, toxins, cancer or other internal disease, or circulation disorder.
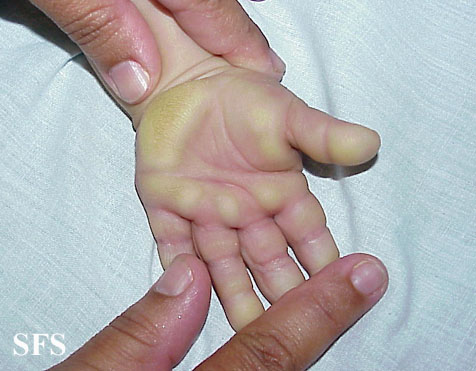
Picture 3. Palmoplantar keratoderma on a child palm.
(source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D., atlasdermatologico)
Treatment includes moisturizing cremes and ointments (containing salicylic acid, vitamin D or retinoids) that help in thinning of thickened skin.
Raynaud’s Disease and Raynaud’s Syndrome
Arterial spasms in Raynaud’s disease and Raynaud’s syndrome may cause itch, tingling, burning or pain.
Chilblains
Chilblains is a cold injury that causes itchy, painful, redish/purplish swelling of the fingers (or the toes, nose, ears). Chilblains may last for several days and may need several weeks to heal completely. Corticosteroid ointment can be used to reduce swelling. Heparin ointment improves circulation (9). Mild painkillers like Aspirin or paracetamol may be used in pain.
Picture of Chilblains on Fingers
Itchy Hand Rash
Rare hand rashes:
- Acrodermatitis continua (dermatitis repens) is considered as a variant of psoriasis, affecting the fingers and toes
- Arthropathic psoriasis
Related Articles:
References:
- Keratosis pilaris – goose skin (dermnetnz.org)
- Treatment of keratosis pilaris (emedicine.medscape.com)
- Itchy upper arm syndrome – Brachioradial pruritus (emedicine.medscape.com)
- Several reports of brachioradial pruritus (thedermblog.com)
- Reports about arm itch (skincell.org/community)
- Pompholyx (dermnetnz.org)
- Hand dermatitis (dermnetnz.org)
- Palmoplantar keratoderma (dermnetnz.org)
- Chilblains (epodiatry.com)