Folliculitis Pictures
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, the tiny tunnels in the skin from which hair grows. It occurs when the hair follicles become irritated and an infection then sets in. This may be seen with damage to the follicle as a result of shaving, friction with clothing, scratching, or an obstruction of a pore.
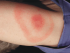
An infected hair follicle appears as a red bump or white pustule which may crust over at a later stage (Picture 1). Infectious folliculitis which arises with a Staphylococcus aureus (bacteria) infection is discussed in detail within this article. Read about other types of folliculitis.
Folliculitis Pictures
Picture of staphylococcal folliculitis on the thigh with red bumps and pus-filled white centers. (Source: Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D., atlasdermatologico.com.br)
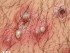
Picture of staphylococcal folliculitis on the chest. (Source: Dermnet)
Folliculitis and Acne
Folliculitis and acne are two different skin conditions although gram-negative folliculitis may be seen in certain cases of severe acne. Acne primarily involves the oil-producing glands (sebaceous glands) of the skin which are clogged with excess oil (sebum) and shed skin cells. It may lead to localized inflammatio which may then develop into folliculitis (Picture 5).
Due to the similarity of the lesions, it may sometimes difficult to differentiate between acne and folliculitis only by visual examination. Some key points to bear in mind though is that acne occurs mainly on the face, neck and upper trunk, more often in teenagers, and may last for months or years. Folliculitis on the other hand may occur anywhere on the body, can affect at any age group, and it usually lasts only for a few days or weeks.
Picture of infected acne. (Source: Dermnet)
Symptoms of Staphylococcal Folliculitis
Staphylococcal folliculitis usually appears as clusters of red bumps surrounding hair follicles (with or without the hair). It varies between 2 to 5 millimeters in diameter, often with a white blister in the center (Pictures 1-3). Inflamed follicles may burst, release pus and crust over. The skin in superficial folliculitis is itchy and tender while in deep folliculitis it may be painful.
Folliculitis most commonly occurs on the :
- Beard area in men
- Scalp
- Upper trunk (chest, under breasts, in armpits)
- Buttocks
- Thighs
- Groin
Folliculitis never appears in areas without hair follicles such as the palms, soles, or mucous membranes. Superficial folliculitis affects only upper parts of a hair follicle, while deep folliculitis affects the whole hair follicle.
Folliculitis Barbae
Folliculitis barbae is a superficial folliculitis of the bearded area in men, caused by Staphylococcus aureus (staph) bacteria. It often appears on the skin around the nose or mouth when hair follicles that are damaged during shaving become infected, especially in those who are nasal staph carriers.
Picture of folliculitis barbae.
Pseudofolliculitis Barbae (Ingrown Hair)
An ingrown hair is a curly hair that curves or twists on the surface and then re-enters the hair follicle opening again. This causes inflammation of the follicle (folliculitis). It may resemble bacterial folliculitis but pseudofolliculitis barbae this is not an infection and tends to occur in those who shave with a razor blade. The use of an electric razor may be one of the preventative measures that may be employed, along with shaving every second day or resorting to not shaving and letting the beard grow (3).
Pictures of Pseudofolliculitis Barbae (Shaving Bumps)
Sycosis Barbae
Sycosis barbae is deep folliculitis of the bearded area in men and involves the deeper parts of hair follicles. Sycosis barbae may leave scars.
Picture of Sycosis Barbae
Stye
A stye is an inflammation or infection of a hair follicle on the eyelid.
Picture of a stye (staphylococcal folliculitis) on the lower eyelid. (Source: Dermnet)
Risk Factors for Folliculitis
Folliculitis is more likely to occur in:
- Nasal staph carriers
- Diabetes mellitus
- Dermatitis
- Obesity
- Topical steroid treatment
- Lowered immunity (leukemia, AIDS)
- Acne treatment with tetracycline
- Infants with tight clothes
- Athletes
- Hot humid climates
Folliculitis Diagnosis
Folliculitis may be diagnosed by a medical doctor without any further tests. However, if there is doubt about the diagnosis, then swabs or biopsies of the skin lesions are collected and sent for laboratory testing. In recurrent folliculitis, diabetes and HIV tests should be considered.
Compare Pictures of Folliculitis with Other Types of Rash
Folliculitis Treatment
- Superficial folliculitis may heal on its own within 1 to 2 weeks.
- Applying over the counter (OTC) antibiotic ointments like Bacitracin, Mycitracin (bacitracin + neomycin + polymyxin B), or Bactrobam (mupirocin), or washing with antibacterial soaps may help in more resistant cases (2).
- In a deep folliculitis and recurrent cases, oral antibiotics (dicloxacillin, cephalosporins) may be needed.
- Folliculitis caused by MRSA requires treatment by antibiotics chosen on the basis of antibiotic sensitivity test (1).
During acute stages, electric razors should be used or shaving should be temporarily avoided in this time. S. aureus carriers may be treated with mupirocin ointment in the nasal vestibule twice a day for 5 days (1). Family members may be also treated by mupirocin to eliminate the carrier state and prevent re-infection.
Is Folliculitis Contagious?
Staphylococcal folliculitis is very contagious. It spreads by direct skin-to-skin contact, or by sharing razors, towels, clothes or other personal items.
Prevention of Folliculitis
The following measures may help to prevent folliculitis :
- Wear comfortable airy clothes.
- Wash and dry swimming suits and sport apparel after each use.
- Eradicate nasal staphylococci.
- Laser depilation for hair removal.
- Disinfect of a sport equipment and hot tubs.
- Do not share razors and towels.
- Apply a disinfectant on any break in the skin with shaving.
Folliculitis Complications
Folliculitis may result in :
- Furuncles
- Cellulitis – inflammation of deeper layers of the skin
- Scars or hyper-pigmentation
- Permanent hair loss (alopecia)
Pictures of Other Types of Folliculitis
Several other types of folliculitis beside staphylococcal folliculitis are known:
- Pictures of Pseudomonas Folliculitis, also known as Hot Tub Folliculitis
- Pictures of Folliculitis Decalvans, also known as Tufted Folliculitis
- Pictures of Scalp Folliculitis
- Pictures of Malassezia Folliculitis, formerly known as Pityrosporum Folliculitis, caused by fungi
- Pictures of Tinea Barbae (ringworm of the beard, barber’s itch, caused by fungi)
- Pictures of Oil Folliculitis
- Picture of Gram Negative Folliculitis (often appears after prolonged acne treatment with antibiotics)
- Pictures of Folliculitis Keloidalis
- Pictures of Eosinophilic Folliculitis (often seen in HIV positive people)
- Picture of Herpetic Folliculitis (in AIDS patients)
Related Articles:
- Staph Skin Infection Pictures
- Types of Skin Rashes
- Itchy Skin
- Jock Itch
References:
- Antibiotics for staphylococcal folliculitis (emedicine.com)
- Antibiotic ointments for folliculitis (bestincosmetics.com)
- Ingrown hair – shaving bumps (aocd.org)