Sleep Reflux (Heartburn) – Causes and How To Prevent It
Waking up at night with a burning chest pain can cause any person to become anxious. The thought of a heart attack may come to mind but often this burning chest pain is related to acid reflux. Heartburn is more likely to occur after eating, especially with overeating or consuming spicy foods. However, some people may experience pronounced heartburn when asleep.
What is sleep acid reflux?
Heartburn is a burning sensation or pain in the chest that occurs with acid reflux. This is a common problem. Heartburn can arise or worsen when asleep due to several physiologic and pathologic reasons. As a result, sleep-related heartburn can affect sleep quality, interrupt sleep or even hamper falling asleep.
Acid reflux, also known medically as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a common gut problem. It happens from infancy right till the senior years. It tends to arise after certain circumstances, such as overeating, consuming spicy foods or with drinking alcohol. However, some people experience reflux on a chronic basis with episodes during which it worsens.

Link between acid reflux and sleep
It is important to look at heartburn and acid reflux in more detail to understand how it may be linked to sleep.
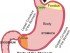
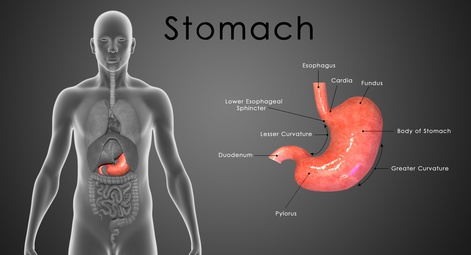
Food that we eat passes down the throat and esophagus (food pipe) to enter the stomach. Between the esophagus (food pipe) and stomach is the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). This prevents enzymes, acid and food in the stomach from flowing backwards into the esophagus. However, the LES sometimes malfunctions.
When this happens, the LES cannot prevent stomach acid, enzymes and food within the stomach from entering the esophagus. This is known as acid reflux or more correctly as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The esophagus cannot contend with the strong stomach acid and powerful digestive enzymes.
These substances then irritate and inflamed the esophagus wall. It causes a burning sensation which we refer to as heartburn. The LES can malfunction for various reasons temporarily like with overeating and alcohol consumption. However, some people have a permanently weakened lower esophageal sphincter and experience chronic heartburn.
There are two main reasons why acid reflux and therefore heartburn worsens during sleep. First, the lying flat position is one factor for sleep-related heartburn. Secondly, the biological clock causes increases in stomach acid during times of the day when most people are sleep.

Causes of Sleep Heartburn
Lying Flat
People with a permanently weakened LES will find that certain positions can immediately trigger acid reflux and heartburn. One of these positions is lying flat, on the back, on the chest or on the sides. Most people with a weakened LES find that it further worsens when lying on the right side. Naturally most people sleep in a lying down position during which reflux and heartburn worsens.
Lying down, whether flat on the back or the side, negates the effects of gravity. This means that the stomach fluids can easily flow into the esophagus. However, this is unrelated to sleep. It can happen even when lying down while wide awake. People with chronic GERD notice that heartburn worsens when lying flat immediately after a meal, especially a large meal.
Read more on reflux when lying down.
Increased Stomach Acid
Stomach acid volume fluctuates throughout the day. It increases after a meal when it is most needed for digestion. However, the stomach acid also rises spontaneously in the early hours of the morning. This is due to the fluctuations related to the body’s 24 hour biological clock, also known as the circadian rhythm.
The stomach acid increases between 1 A.M. and 4 A.M. and this can increase reflux and heartburn during these hours. Once again, it is not sleep-related but rather due to timing. Most people are asleep during these hours. Therefore this early morning acid reflux is referred to as a sleep heartburn.
Eating Before Bedtime
A common practice that can lead to acid reflux while asleep is eating before bedtime. People with chronic GERD should avoid this practice.The stomach becomes active after meals. This means strong muscle contractions to churn and breakdown food in the stomach.
However, if the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) is weak and a person lies down after a meal, then acid reflux while sleeping is more likely to occur. Once again, it is not sleep related but rather due to eating before bedtime and the subsequent position of the body.
Alcohol To Sleep
A nightcap may have the opposite effect than what is intended. Alcohol further weakens the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). People with chronic GERD need to avoid alcohol prior to sleeping as this exacerbates the problem. Here as well, the problem is not sleep but rather the position and the compounded effects of alcohol on the LES.
How to Prevent Sleep Heartburn
There are a few simple ways to prevent sleep-related heartburn. This will not always be effective to avoid sleep heartburn altogether but it can be helpful. In some cases, medication like antacids or acid-suppressing drugs like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are necessary to minimize acid reflux and heartburn while asleep.
- Avoid eating before bedtime. A gap of at least 3 hours between the last meal and bedtime is ideal. Opt for water rather than tea or coffee before going to bed. Waking up to snack should be avoided at all costs.
- Use a specially-designed wedge to slightly elevate the upper torso. Using an extra pillow can help but may strain the neck. Sometimes elevating the head of the bed may also be beneficial if a wedge cannot be sourced.
- Do not consume alcohol prior to bedtime due to its effects of weakening the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). However, even non-alcoholic drinks like cocoa or hot chocolate may also contribute to sleep heartburn and should be avoided if it poses a problem.
- Do not eat spicy foods or any other trigger foods for dinner. Even if dinner is many hours before bedtime, problem foods can trigger or aggravate acid reflux for long hours and extend into sleeping time.
- Alkaline drinks like milk can help but the effect is very short-lived. Antacids that neutralize the stomach acid may have a longer lasting effect and should be taken before bedtime.