Causes of Arm Pain – Right and Left Pain in the Arms or Hands
Pain, in any part of the arm, is a common complaint and may be caused by various factors. The dominant arm (the arm and hand most used), usually the right arm, is more prone to pain, injury and strain, especially if the arm has to perform repetitive activities. While arm pain may not always appear to be a serious condition, it could be indicative of a major underlying pathology that requires emergency medical treatment.
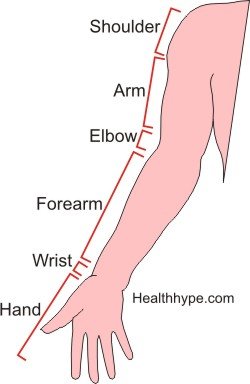
The upper limb is often referred to as the arm or hand however these are only sections of the limb. Anatomically the upper limb includes the following structures :
- Shoulder
- Arm (area between the shoulder and elbow)
- Elbow
- Forearm (area between the elbow and wrist)
- Wrist
- Hand
For the purpose of this article, we will refer to the upper limb as the arm.
Types of Pain
Pain is a sensation that usually occurs as a result of injury or damage to living tissue and causes discomfort or distress, depending upon the severity. It may be constant or intermittent with varying intensity that depends on individual tolerance and extent of injury. Arm pain may be one sided or affect both arms simultaneously. Pain is a subjective experience and encompasses a number of different types of pain that may be described as a :
- dull ache
- throbbing or pulsating pain
- shooting pain
- burning pain
- pinching pain
- poking or stabbing pain
The arm (upper limb) is made up of a number of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments, along with their various nerve supplies, and all are susceptible to injury and damage that can lead to pain. However at times, pain in the arm may be caused by a damage at a distant point and this is known as referred pain.
The upper limb is mainly composed of muscle and bone and muscle pain is a common type of arm pain that often occurs after strain or exertion. Joint pain may affect the shoulder (e.g. frozen shoulder), elbow (e.g. tennis elbow), wrist (e.g. carpal tunnel syndrome) or the small joints of the fingers (e.g. rheumatoid arthritis). There is another type of pain which seems to come from a body part that has been removed, such as an amputated hand or leg, and this is called phantom pain.
Neuropathic or nerve pain may be due to degeneration of the nerve, as in a stroke, multiple sclerosis or from nerve compression (pinched nerve), nerve inflammation, or infection of the nerve (shingles), where pain can be severe. Psychogenic pain is the perception of pain with no clear cause, often a result of psychological factors like anxiety.

Causes of Arm Pain
Arm pain may be due to many causes, ranging from s simple injury to more complex causes like the arm pain arising from a heart attack (myocardial infarction). While the arm is only one section of the upper limb, the area between the shoulder and elbow joint, the entire upper limb is commonly referred to as the arm or hand. In order to determine the cause of arm pain, it is important to identify any incidents that preceded the onset of the pain and take into consideration the medical history. This will allow for a more definitive diagnosis of the cause of the arm pain, although this is a common symptom that affects many of us at some point in our life.
Joint Pain
Arthritis is a generalized term referring to inflammation of a joint and the symptoms most commonly produced are pain, swelling, and restricted joint mobility. There are various types of arthritis, including osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, the latter being more likely to cause arm pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease which leads to the inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It may occur at any age, with women being affected more often than men. Joints of the fingers, wrist, knees, ankle and feet are likely to be involved. There is usually bilateral (both sides) involvement of joints, occurring in a symmetrical pattern causing joint pain and stiffness. Rheumatoid factor test, or a specific blood test to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis and differentiate it from other types of arthritis, called the anti-CCP antibody test, may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
- Osteoarthritis is a slow progressing, degenerative joint disease, which occurs more frequently in older people. It may be limited to or start in one joint, such as the knee, hip, or hands, or it may involve a number of joints. If it affects the hands, multiple joints of the fingers are likely to be affected. Osteoarthritis may be hereditary, or it may be due to repetitive actions or overuse, injury, or muscle strain.
Gout is a disorder where there are high levels of uric acid in the blood and tissues. Uric acid crystals are deposited in the joints, causing gouty arthritis, which can be an extremely painful condition. It normally affects the big toe, but may also affect the wrist and fingers, causing swelling, redness, and severe pain in the fingers and wrist joints.
Referred Pain and Nerve Pain
Referred pain is pain felt in one area of the body when the actual cause is in some other part. The exact cause of referred pain is not known but may be due to signals from different areas of the body traveling through the same nerve pathways in the brain and spinal cord. Nerve pain or neuropathic pain is the pain experienced along the course of the nerve due to injury, inflammation or degeneration of the nerve. Nerve compression or pinched nerve pain is an example of neuropathic pain.

- Myocardial infarction or a heart attack typically causes chest pain (sometimes described as a breast bone pain) although other symptoms may accompany this medical emergency, including upper middle abdmoinal pain (epigastric pain), sweating, nausea, vomiting, or pain in the jaws, neck, or the characteristic left arm pain, although there may be referred pain in the right arm.Early diagnosis is vital because heart attack with even mild symptoms may become life-threatening, hence the possibility of a heart attack should always be kept in mind in case of pain in the arm with or without chest pain. An ECG (electrocardiogram) and blood tests for cardiac enzymes must be done on the slightest suspicion that a heart attack is occurring so that a quick diagnosis and appropriate medical treatment can be initiated.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition which develops due to compression of the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel at the wrist. It gives rise to symptoms of pain and paresthesia (arm numbness and tingling or “pins and needles” sensation) along the distribution of the median nerve , which includes the nerves supply to the thumb, index, middle, and half of ring finger.
- Radial tunnel syndrome is caused by the compression of the radial nerve in the forearm, leading to pain along the distribution of the radial nerve in the hand. The symptoms are similar to those of tennis elbow, such as pain at the back of the forearm and elbow.
- Cubital tunnel syndrome occurs due to compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow. Prolonged flexion of the elbow or leaning on the elbow for a considerable time can produce this syndrome, causing pain and numbness along the distribution of the ulnar nerve, especially in the ring and little finger.
- Cervical radiculopathy or pinched neck nerve may occur due to a damaged intervertebral disc in the cervical or neck region of the vertebrae and may be the cause of hand pain. Depending upon the severity of nerve damage, there will be symptoms such as tingling and numbness, “pins and needles” sensation, or burning pain in one or both arms. Refer to the article on Pinched Neck Nerve.
- A cervical rib is an extra rib, just above the first rib, that may be present at birth. It may cause arm pain if it presses upon the brachial plexus, which is a bundle of nerve fibers that controls muscle movements and sensation of the shoulder, arm and hand.
- Phantom pain is a type of neuropathic pain which arises from an amputated body part, such as a leg or arm. Although initially thought to be a psychological phenomenon (psychogenic pain), this sensation is now understood to originate from the brain and spinal cord. Phantom pain in the amputated arm can start within a few days of amputation of the hand, either due to trauma or surgery, and may be experienced as a shooting, stabbing, squeezing, or throbbing type of pain. This pain may seem to originate from the distal (farthest) part of the amputated arm, such as the fingers, and may be initiated by emotional stress or pressure on the remaining part of the hand.
Pain from the Breast
Breast pain may occur due to many causes and it can travel down to involve the arms and hands. Since chest pain radiating down to the arms can be a symptom of angina or myocardial infarction, and may be confused with arm pain caused by breast problems, it is important to differentiate between the conditions so that proper treatment can be initiated without loss of time.
- Cyclic breast pain typically starts about a week before the menstrual period and gradually decreases with the onset of menstruation. Pain is bilateral (in both breasts), dull and aching in nature, and often radiates down to the armpit or inner side of both arms.
- An infection in the breast (mastitis), if left untreated for long, may spread to other areas such as the armpit and upper arms and result in arm pain. Typically, swollen lymph nodes will be noted in and around the affected area.
- In the initial stages, breast cancer may not produce any symptoms of pain, but in later stages, with the development of a palpable lump in the breast, pain may be felt in the breast itself, the armpit and/or along the arm. Breast cancer can also cause severe pain in the arms by affecting the nerves in the spinal cord or by spread of cancer to the lymph nodes around the nerves.
- Breast cancer patients who have had axillary (armpit) surgery often suffer from chronic pain in the armpit, shoulder and upper arm and this pain seems to be related to the extent of the axillary surgery.
Ganglion
Ganglion is a small swelling or cyst that develops from the tissue lining a joint or tendon. The cause is usually unknown, but may sometimes be due to a local trauma to the joint or tendon. Recurring or persisting ganglion could be an early sign of arthritis. A ganglion is commonly found at the back or front of the wrist and symptoms may include a slow growing cystic swelling, which may or may not be painful, along with mild pain at the wrist.
Tendon Disorders
A tendon is the thick cord of tissue which connects a muscle to a bone. Arm pain may be caused by tendonitis (inflammation of a tendon) or tenosynovitis (inflammation of the lining of the tendon sheath which encloses the tendon). Rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, overuse, injury, strain, or overexertion may lead to tendonitis or tenosynovitis, most often affecting the fingers or wrist, and causing symptoms such as swelling, pain or discomfort.
- Tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis is a frequent cause of arm pain and is caused by damage of the tendons involved in bending the wrist backwards, away from the palms. There may be recurring pain at the back of the forearm and elbow when the arm is at the side of the body with the thumb turned away. Lifting or bending the arm or grasping even light objects may cause pain in the arm and/or hand.
- Golfer’s elbow (baseball elbow) or medial epicondylitis is caused by damage of the tendons involved in bending the wrist towards the palm. This is another strain related condition causing arm pain which may be mistaken for tennis elbow, but in this case the pain is felt on the inner side of the forearm, extending from the elbow to the wrist.
- Rotator cuff tendonitis is caused by inflammation of the shoulder capsule and associated tendons. There is usually a dull, aching pain in the shoulder which may radiate to the upper arm or chest, often getting worse at night. It may often occur due to overuse, such as during a sport or work related activity, which requires the arm to be lifted repeatedly, and will affect the dominant hand, example right shoulder in a right-handed person.
- De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the tendon sheaths on the thumb side of the wrist, causing pain and discomfort on trying to turn the wrist, grasp something, or when making a fist.
- Trigger finger or trigger thumb is inflammation of the tendon sheath of a finger or thumb causing pain, swelling, and difficulty in flexing or extending the finger or thumb.
Trauma
Injury to any part of the upper limb can result in pain and may continue long after the incident. Trauma may vary from soft tissue injury to breaks in the skin, muscle damage, fractures of the bone or even loss of part of the arm. The cause of the injury is clearly evident and even after the area is treated or heals, pain may persist for months or years.
- Muscle strain is the stretching or tearing of muscle fibers (torn muscle), often due to overworking a fatigued muscle, and occurs most frequently during sports activities. However, it may also occur while carrying out simple activities such as stepping off a curb or by carrying many heavy bags in the hand. Muscle strain in the hand will cause mild to severe pain in the affected arm along with swelling and decreased strength.
- A sprain is an injury involving a tear or stretching of ligaments which arethe tough fibrous bands which connect bones to one another at a joint. A sprain in the hand may be caused by flexing the hand suddenly or by falling on an outstretched hand. It can occur by slipping and falling on the wrist or shoulder. Any unusual force across a joint can cause a sprain and often occurs during sporting activities. There will be pain, swelling, and instability of the joint.
- Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa, a small pouch between the bone and tendon. This can affect the elbow or shoulder joint and causes severe pain, without any loss in range of motion. Adhesive capsulitis or frozen shoulder is the inflammation of the capsule surrounding the shoulder joint. While both bursitis and a frozen shoulder can cause arm pain, in a frozen shoulder, the range of motion is severely restricted.
- Fractures of one or more bones of the arm are among the most common types of fracture and may occur in all age groups. The severity of pain will depend on the type and site of fracture and other associated injuries.
- Writer’s cramp is another type of arm pain commonly affecting the dominant hand, since this is the hand most often used for writing. It is caused by overuse of the hand in small fine movements, like writing, and may be due to the position of the hand during writing, gripping the pen, pencil or tool too tightly or continuous use or writing for long periods of time.
Infection
Cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection, which normally starts with infection of the skin, caused most often by Streptococcus pyogenes or Staphylococcus aureus (Refer to Staph Infection Symptoms). Bacteria usually penetrate the skin at the site of injury, such as a cut or puncture in the skin, and causes an infection, which then spreads to other tissues.
This typically causes swelling, severe pain, heat or increased temperature of the skin and/or redness of the skin. Cellulitis is common in the hand as it is used for most activities, especially the dominant hand, so chances of injury and infection are high. Surgery on the arm or intravenous catheterization of a vein in the hand for the purpose of administering I.V. drugs or fluids may also become the initial site of infection leading to cellulitis.
Vascular Disorders
Raynaud’s phenomenon is a rare condition where there is extreme response of the blood vessels in the skin to a cold environment, resulting in severe constriction of the blood vessels (vascospasm), especially those of the fingers and toes. The affected skin turns white from loss of blood, then blue from lack of oxygen, and there is associated tingling and numbness. This phenomenon is temporary and reversible on applying warmth, which causes the skin to turn pink along with a throbbing sensation.
Psychogenic Pain
This type of pain arises from mental or emotional stress and is a perceived sensation that is usually not detectable even by a nerve conduction study. It typically occurs in persons with a type A personality, concerned about a heart attack, or in cases of anxiety, where a stressful incident may trigger the pain.
Arm Pain Symptoms
Hand pain may be accompanied by other signs and symptoms. Some of these concomitant symptoms include :
- muscle weakness
- twitching
- cramps
- swelling (refer to Arm Swelling)
- itching
- heat
- change in skin color
- increased skin temperature
While intense pain may mask other sensations, it is possible to experience pain on one part of the arm and other sensations like arm numbness or tingling elsewhere on the upper limb. At times, these concomitant signs and symptoms that accompany arm pain may not affect the upper limb only, like sweating, dizziness or blurred vision associated with the arm pain that occurs during a myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Acute or Chronic Arm Pain
Arm pain may be acute or chronic, depending upon its duration. Acute pain is of sudden onset and may be intense and short-lived, often due to injury. Chronic pain develops insidiously and may be of long duration, and is more likely to be due to conditions such as nerve compression. The pain may also be persistent or occur in episodes and if episodic, it is important to note factors that trigger, aggravate or precede the pain.
Arm Pain Diagnosis
In order to diagnose the possible causes of arm pain, your doctor will take a case history, conduct a physical examination and may request other diagnostic investigation techniques. To assist with arm pain diagnosis, it is important to report the exact site (location) of the pain, severity of the pain on a scale of 1 to 10, type of pain, duration , other signs or symptoms accompanying the arm pain and any incident that may have caused the pain or trigger factors.





