Staph Infection Symptoms
Staph Infection Symptoms
Staph infection symptoms include various skin changes, symptoms of infected internal organs, and symptoms related to staph blood poisoning (sepsis).
What is Staph?
Staph infection is caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus (staph for short) and rarely by S. epidermidis or other staphylococcal species.
What is s Staph Infection?
A staph infection is an inflammation of the skin or internal organs, caused by the staph bacteria or its toxins. Staph infection may be mild, severe or even life threatening, and may appear as:
- Skin infection
- Infection of the mucous membranes (sinusitis, epiglottitis, vaginitis)
- Infection of the glands (mastitis, parotitis)
- Staph food poisoning
- Urinary infection in men
- Bone infection (osteomyelitis) and joint infection (arthritis)
- Staph pneumonia
- Bacterial endocarditis
- Staph meningitis
- Bacteremia, sepsis
- Soft tissue gangrene and gas gangrene
- Staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome (SSSS)
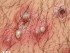
Symptoms of Staph Skin Infection
Staph skin infection may appear as a:
- red skin rash, pus-filled blisters or as folliculitis (refer to folliculitis pictures)
- red bump or swelling on the eyelid (stye)
- vesicles that burst and crust over (impetigo)
- painful red swelling or vesicle around the nail (paronychia)
- painful red nodules which may ooze pus (boils: furuncle, carbuncle)
- swollen red skin patch, usually on the limbs (cellulitis)
- skin scalding, mostly in young children (staphylococcal scalding skin syndrome)
- infected acne, hydradenitis suppurativa or pilonidal cyst
- infected wound, and related infection of lymphatic vessels (staphylococcal lymphangitis)
For a detailed description, read more on staph skin infections with pictures.
Symptoms of Staph Mastitis
Staph mastitis is an inflammation of the mammary gland mostly occurring in breastfeeding mothers within 6 weeks after childbirth or sometimes later(1). Symptoms of mastitis may include:
- Red, warm, tender or painful swelling or a lump in the breast (usually only on one side)
- Breast skin and nipple itch
- Nipple discharge
- Fever over 101°F (38.3°C), feeling ill
- Tender or enlarged lymph nodes in related armpit
Symptoms of Bacterial Parotitis
Bacterial parotitis is an inflammation of the parotid gland (the salivary gland lying under the skin below the ear) caused by staph or other bacteria. It usually occurs in old, dehydrated patients or those who were intubated (2). Bacterial parotitis has to be distinguished from viral parotitis which mostly occurs in children. Both types are usually one-sided and are rare. Symptoms of bacterial parotitis usually include:
- Painful swelling bellow the ear on one side
- Painful mouth opening (trismus) and swallowing (dysphagia)
- Thick discharge into the mouth
- High fever with chills
Staph Food Poisoning Symptoms
When a person responsible for food preparation has staphylococci in the nasal cavity (staph carrier) or has staph skin infection, some bacteria may end up in the food. If such food is kept outside the refrigerator for few hours, bacteria may produce enough toxins to cause food poisoning.
Symptoms of staph food poisoning are:
- Nausea and vomiting, appearing between 30 minutes and 8 hours after food ingestion
- Rarely, diarrhea or fever, which follow the vomiting
The illness usually lasts for one to three days and resolves on its own without consequences.
Bacterial Sinusitis Symptoms
Bacterial sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucosa, which covers the inner surfaces of the bone cavities (sinuses) around the nose. It may be caused by staph or other bacteria.
Symptoms usually include :
- Pain in cheeks, teeth, or forehead
- Blocked nose, changed smell, sticky greenish nose discharge, bad breath and, rarely, fever
- High fever, facial swelling, severe headache, neck stiffness and confusion in severe sinusitis.
Bacterial sinusitis usually lasts for more than 10 days, while viral sinusitis usually resolves in few days on its own.
Bacterial Epiglottitis Symptoms
An epiglottis is a cartilage on the base of the tongue, which prevents the entrance of food into the larynx during swallowing. Injury of epiglottis’s mucosa may be followed by severe, life threatening staph infection, characterized by:
- Sudden severe pain in the throat
- Painful swallowing
- Excessive salivating
- Difficult breathing, air hunger
- High fever
Bacterial epiglottitis is rare, mostly seen in young children, rarely in adults (3).
Staph Vaginitis Symptoms
Symptoms of staph vaginitis may include:
- Purulent discharge (blood may be present) with bad (fishy) odor
- Pain during intercourse or urinating
- Vaginal itch
Symptoms of Bacterial Urinary Infection in Men
Various staphylococci species and other bacteria may cause infection of urinary system in a male.
Common symptoms are:
- Burning pain during urination, urinary frequency and urgency.
Symptoms of bacterial prostatitis:
- Pain in the groin, testicles, penis or lower abdomen
- Cloudy urine, rarely blood in the semen
- Fever and muscular pain.
Kidney infection (pyelonephritis) and infection of the bladder (cystitis) are characterized by:
- Pain over the kidney(s), lower abdominal or lower back pain (in cystitis)
- Cloudy urine
- Fever with chills.
Urethritis, epididymitis, orchitis and urinary infections in women are only rarely caused by staphylococci (4).
Staph Bone Infection (Osteomyelitis) Symptoms
Staph bone infection (osteomyelitis) typically occurs in children and most commonly affect the lower end of the thigh bone, the upper end of the lower-leg bone (tibia), upper-arm (humerus) or fore-arm (radius) bone.
In staph osteomyelitis there are often no symptoms. When an infection was due to injury, a skin redness, swelling or ulcer may appear on the site of injury. Severe pain and fever are common and mobility of the limb is usually affected. Lymph nodes lying between a bone infection and the heart may be swollen (5). The ulcer may heal slowly and drain pus. Infection may spread into an adjacent joint.
When staphylococci reach the bones by blood (hematogenous spread), swelling, pain and redness may appear on the skin above the affected bone (including the spinal vertebra or pelvis – in older patients)
Staph joint infection (arthritis) may arise from an infection of an adjacent bone, a direct puncture of the joint (usually knee in children) or from spread of staphylococci by blood .
Symptoms of staph arthritis include:
- Infected joint is swollen, red, warm and extremely tender (6)
- Fever
Symptoms of Life Threatening Staph Infections
Staph Pneumonia Symptoms
Staphylococcal pneumonia typically occurs in hospitalized patients (hospital acquired pneumonia) with an underlying lung disease, intravenous drug addicts and persons with indwelling prosthetic devices (7). Symptoms do not differ from pneumonia caused by other bacteria and usually include :
- High fever and chills
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Cough
- Cyanosis – bluish skin
Bacterial (Staph) Endocarditis Symptoms
Staph endocarditis usually results from the spread of Staphylococcus aureus from the skin in intravenous drug users, or in children with inborn heart disease, prosthetic valves, or after inserting venous catheters or surgery. Symptoms of bacterial endocarditis are not specific and may include :
- Fever, rarely exceeding 39°C
- Paleness
- Fatigue, night sweating, joint/muscular pain
- Splinter hemorrhage under the nails, red skin spots on the palms and soles (Janeway lesions), red, painful nodes on the fingers and toes (Osler’s nodes), tiny mucosal bleeding (petechia) in eye conjunctiva (8)
- Heart murmurs may be sometimes detected by a stethoscope (8)
Complications of bacterial endocarditis may include :
- Acute heart failure – breathlessness, leg and belly swelling, enlarged liver and spleen may appear
- Stroke – muscular activity and sensations may be affected
Staph Meningitis Symptoms
Staphylococcal meningitis may occur in patients after brain surgery or severe skin infections.
Symptoms are like in meningitis caused by other bacteria:
- Low grade fever
- Headache
- Lethargy
- Confusion
Signs of meningeal irritation like neck stiffness are usually not present (9).
Bacteremia, Septicemia
Bacteremia is the presence of bacteria in the blood. Bacteria may enter the blood from the site of infection, like pneumonia or meningitis, during inserting vascular catheters, drug administration, surgery, tooth extraction, and so on. Temporary bacteremia may following brushing teeth vigorously or entery of bacteria from the intestine, and it is not dangerous, since bacteria are quickly destroyed when they pass the liver (11). Symptoms of bacteremia include :
- Fever or middle ear infection (in children), but no other symptoms (10).
Tooth extraction in a patient who has staphylococci in mouth and has congenital heart disorder or prosthetic heart valves may lead to bacterial (staph) endocarditis.
Sepsis (inflammation of the blood) is bacteremia with symptoms (13). Staph sepsis is usually triggered by staph bacteria entering the blood from an existing infection, like infected skin burns. Sepsis may be a life threatening condition. Symptoms of staph sepsis (11,12,13) are:
- Sudden high fever with or without chills or hypothermia in a patient with existing staph infection
- An affected person looks seriously ill, feels weak, and may have nausea, vomiting or diarrhea
- Rapid heart beat and rapid breathing
- Symptoms arising from affected organs (osteomyelitis, arthritis, meningitis, endocarditis, pericarditis, and so on)
Septicemia may lead to shock with altered consciousness, hypothermia, red spots on the skin (from bloody clothing), shallow breathing and decreased urination.
Necrotizing Soft Tissue Infections
Necrotizing soft tissue infection (necrotizing fasciitis, soft tissue gangrene) is a rare, severe bacterial infection, caused by staphylococci, streptococci or other bacteria, which can destroy the muscles, skin, and underlying tissue (14).
A small red spot or bump may appear on the skin and changes into a painful brownish, purple and finally black patch, which may ulcerate and drain fluid or pus, may develop. The wound may develop in less than an hour. General symptoms may resemble sepsis. Without treatment, death may follow quickly.
Gas Gangrene
Gas gangrene may develop in a wound infected with S. aureus or Clostridium perfringens bacteria, often in persons with atherosclerosis or diabetes. Gas gangrene differs from the above mentioned soft tissue gangrene by the following symptoms:
- Gas may be felt around the wound edges
- Brownish-red skin patch or blisters may appear around the wound
- Moderate pain and moderate fever develop
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome is a severe illness caused by toxins released from S. aureus bacteria, and may follow any existing staph infection. It mostly occurs in women using tampons or diaphragm, or as a complication of a nasal surgery or staph wound infection (15).
Symptoms of toxic shock syndrome may include (15) :
- Sudden onset of high fever, vomiting, diarrhea and muscle pains
- Sunburn-like skin rash, which peels off in 1-2 weeks
- Shock may develop; disease is fatal in about 5% of cases
References:
- Mastitis (nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus)
- Parotitis (ucsf.edu)
- Epiglottitis (emedicine.com)
- Urinary infections in men (emedicine.com)
- Osteomyelitis (kidshealth.org)
- Hospital-acquired pneumonia (merck.com)
- Bacterial endocarditis (nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus)
- Staph meningitis (emedicine.com)
- Bacteremia (emedicine.com)
- Temporary bacteremia, sepsis (merck.com)
- Sepsis (nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus)
- Sepsis (emedicine.com)
- Soft tisue gangrene (nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus)