Leg Weakness – Causes and Treatment
Leg weakness is a serious symptom which is commonly ignored by many people. It is highly based on individual perception initially but may eventually progress to a point where the legs ae not able to function properly and there may even be paralysis .Leg weakness is frequently accompanied by loss of sensation (leg numbness) or leg pain, which often arise before the weakness.
What is leg weakness ?
Leg weakness is the weakened strength of the leg muscles, which is manifested by inability to do certain movements with the foot or leg. Weak legs should not be confused with tiredness or a heavy feeling that occurs with strain from prolonged standing or physical activity.
It should also not be confused with muscle cramps or arthritis which cause pain with movement and limited range of movement. Leg weakness also interferes with walking especially when it is involving the foot muscles. This is known as foot drop, in which a person is unable to lift the foot upwards.

Causes of Leg Weakness
The leg is supplied by nerves which come out of the spinal cord and back bone in the lower part of the back. These nerves travel all the way from the lower back to the various parts of the leg. Sensory impulses are relayed from the different parts of the leg to the brain while motor impulses from the brain are relayed to the leg muscles via these nerves. These nerve problems are collectively referred to as peripheral neuropathy.
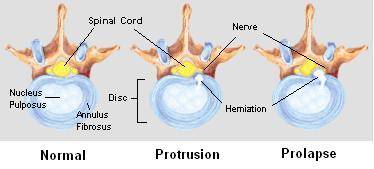
The vertebrae in the lower part of the back are a common site of diseases like slip disc (slipping of cartilage intervertebral disc ) which normally lies between two vertebrae (spinal bones). This can cause compression of spinal nerves which is also known as nerve root compression commonly referred to as a pinched lower back nerve. It is commonly seen in conditions like sciatica where the sciatic nerve is compressed.
There are also various diseases that can cause nerve problems, like diabetes mellitus which leads to diabetic neuropathy. The nerve damage caused by these diseases results in abnormal functioning of the areas supplied by the nerves. It can cause muscle weakness, loss of sensation or both. However, various muscle problems may also be responsible for leg weakness even if the nerves are intact. These conditions are broadly referred to as myopathies.
Read more on causes of weak legs.
When is leg weakness an emergency?
Nerve damage is almost always permanent as nerve tissue does not regenerate. Depending on the cause, there is a window period of a few days between the onset of leg weakness and pemanent damage of the nerve. Therefore rapid medical treatment is necessary to prevent or reverse this permanent nerve damage where possible. While weakness or paralysis is serious, it may not always be seen as an emergency since the legs are not a vital organ.
Sometime leg weakness may be due to serious condition like a brain stroke. Normally this affects only one leg (unilateral weakness or paralysis). A stroke is potentially fatal. Therefore when leg weakness arises suddenly, is one sided and accompanied with symptoms like arm weakness and facial muscle weakness (usually on the same side) then immediate medical attention is necessary.
Diagnosis of Leg weakness
Leg weakness most commonly arises from nerve compression in the lower back. Therefore pain in the lower back region should not be ignored, especially if it is long standing. The shooting pain, which travels from the lower back to the knee or the ankle, is because of the irritation of the nerves caused by compression. This is also known sciatica because the sciatic nerve divides into smaller nerves which supply the leg muscles and also provide touch sensation.
The initial assessment consists of evaluation of the leg muscles by a doctor or a physical therapist. Several simple movements to measure the muscle strength and activity can confirm leg weakness but not a specific cause. However, various diagnostic investigations are necessary to identify the underlying cause.
Read more on the signs of nerve damage.

The common diagnostic tests employed for investigation of causes of leg weakness are:
- X-rays of lower back, which rule out bony abnormalities like fractures or spondylolisthesis (forward or backward slipping of a vertebra). This is the primary investigation for all causes and is especially important when one has had a traumatic incident like a fall or a road accident.
- MRI helps in diagnosis of injuries and abnormalities like slip disc, intervertebral disc protrusion, nerve compression, and so on. Soft tissues which cannot be seen on x-rays can be seen on MRI so the causes related to them can be accurately diagnosed.
- Nerve conduction studies are used in diseases, which are difficult to visualize on X-ray or MRI, and which are confined to the nerves. In this test, small electrodes are stuck to the different parts of the body and measurements are made of the electrical activity of the nerves of that part.
After these investigations and the physical examination, leg weakness can be attributed to compression of spinal cord, compression of spinal nerve or local nerve disease.
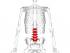
Spinal Cord Compression
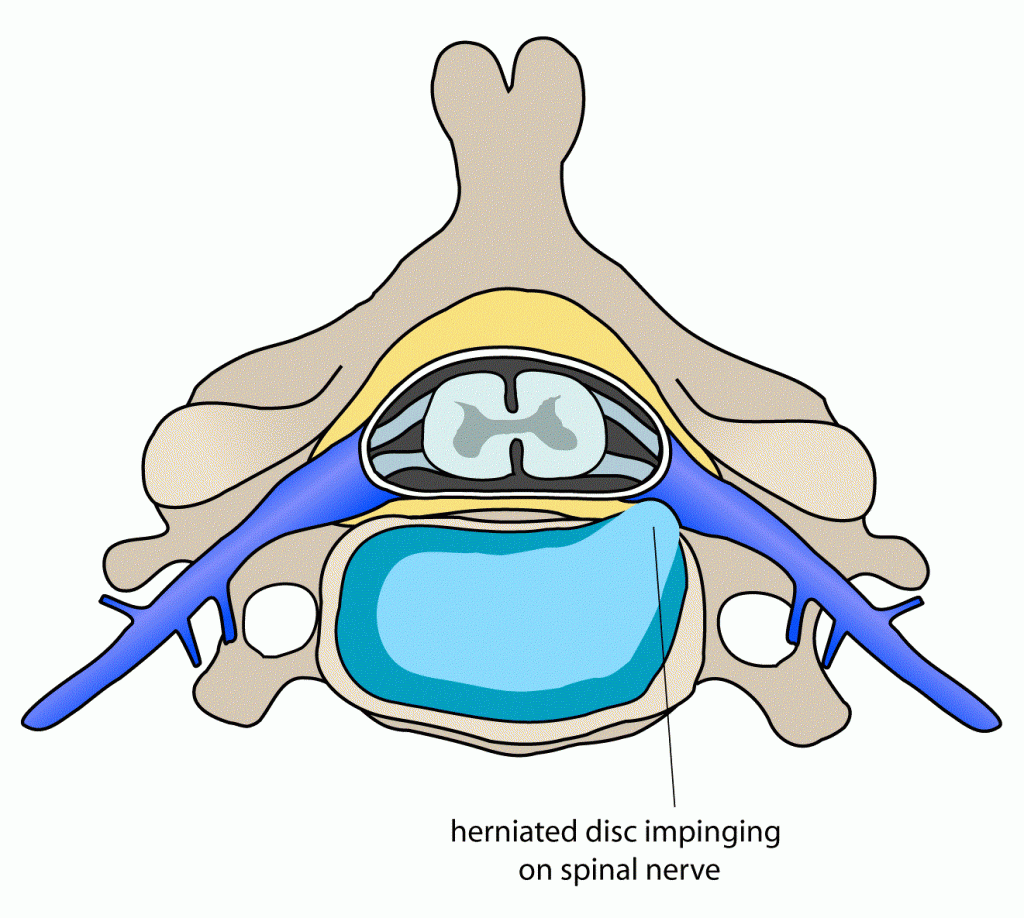
Compression of spinal nerve or spinal cord is mostly due to intervertebral disc protrusion. However, some other causes for the same are spinal tumor, sciatica, dislocation of vertebra (spondylolisthesis), fracture of vertebra, and spinal stenosis. Local nerve diseases like multiple sclerosis, leprosy, syphilis, or neurofibroma may also be responsible for leg weakness if it involves the sciatic nerve. Nerve injury due to trauma, like a motor vehicle accident or fall, can also damage or even sever the nerve.
Treatment of Leg weakness
Leg weakness due to local nerve disease is treated according to the underlying caue. Most of these diseases are treated with medication and may required surgery as well. Leg weakness caused by spinal cord or nerve compression are treated by surgery.
Diseases like sciatica and fracture of vertebra are generally treated with bed rest and painkillers for a period of at least 6 weeks. This is followed by exercises and physical therapy which strengthen the muscles and reduce pressure on the nerves. Medication is mainly for pain management and muscle relaxants may also be prescribed.
Read more on types of nerve injury treatment.
The surgery for spinal tumor or intervertebral disc protrusion should be taken only when leg weakness or loss of sensation is present. A person also has to wear an orthosis (a belt for the back which gives support and restricts some movement) after surgery for a long period of time.
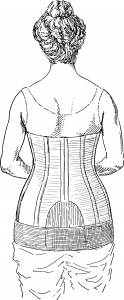
Orthosis for lower back
The surgery of spinal cord or vertebral column is not entirely without risk. There is even the risk of paralysis after the surgery. In the presence of leg weakness, surgery is the preferred option, especially if there is risk of paralysis without the surgery. However, conservative measures and medication may be considered if there is no leg weakness or other serious symptoms.
References
- Myopathies. Medscape
- Weakness. MSD Manual