Trouble Breathing Causes, Symptoms, Signs
Signs and Symptoms of Breathing Trouble
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is the most common symptom of any problem with the respiration process.
Refer to the articles on :
Other signs and symptoms may include :
- Flaring of the nostrils.
- Abnormal expansion of the chest cavity.
- Faster breathing rate (tachypnea).
- Changes in skin color, especially of the face – starting with red flushing and progressing to a pale discoloration (pallor) to bluish tinge (cyanosis).
- Abnormal breathing sounds – wheezing, stridor, gasping or grunting.
- Sweating.
These signs and symptoms are indicative of respiratory distress and should be treated as a medical emergency.
Causes of Breathing Trouble in Different Situations
Trouble Breathing Deep, In, Out
This includes trouble breathing in deep (deep inhalation) or uncomfortable or impaired inhalation and exhalation.
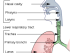
- Partial or complete narrowing of the air passages – for example, asthma, lung tumor, bronchitis.
- Weak respiratory muscles due to muscular or neurological conditions – for example myasthenia gravis, diaphragmatic paralysis.
- Diminished lung elasticity – for example chronic bronchitis, emphysema.
- Lung inflammation – for example interstitial lung disease, pneumonia.
- Chest wall injury – for example fractures rib or sternum.
- Fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema) or around the lungs (pleural effusion) – for example congestive cardiac failure, pleuritis.
Chest Pain, Trouble Breathing
While any breathing difficulty should be treated seriously, any chest pain with trouble breathing should be considered as a medical emergency.
- Heart muscle ischemia, infarction – for example angina, heart attack (myocardial infarction).
- Heart muscle inflammation – for example myocarditis.
- Lung and pleural lining inflammation – for example pneumonia, pleuritis.
- Airway inflammation, infection – for example bronchitis, tracheitis.
- Trauma to the chest wall – for example fractured rib(s), costochondritis.
Refer to Lung Chest Pain, Heart Chest Pain, Bone Chest Pain and Muscle Chest Pain for more information.
Trouble Breathing with Acid Reflux, GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or acid reflux can trigger chest pain (not just a burning sensation) and this stimulates nerve networks in the area. Common nerve fibers can stimulate constriction of the muscles in the air passages thereby narrowing the airway. This will result in shortness of breath. Severe cases of GERD could result in tracheal aspiration where some of the gastric contents enter the air passages. This causes inflammation of the air passages, which results in swelling and therefore narrowing of the airway.
Refer to Gastric Chest Pain for more information.
Trouble Breathing with Anxiety
Shortness of breath in anxiety is a common symptom and the breathing difficulty may only be a perceived sensation. It can sometimes lead to hyperventilation. Patients with conditions like asthma may experience a narrowing of the airway during an anxiety attack or when under stress.
Allergies and Trouble Breathing
The action of immune chemicals associated with allergic reactions, like histamine, can cause a swelling of the lining of the air passages. This swelling narrows the air passages. Refer to Angioedema. Simultaneous excessive mucus secretion by the air passage lining will further affect the flow of air through the air passages.
Trouble Breathing when Lying Down
- Diminished lung elasticity – for example in COPD like emphysema.
- Cardiac conditions – for example in heart failure, cor pulmonale.
- Fluid in the lungs – for example in congestive cardiac failure (CCF).
- Reduced space or weight hampering lung expansion – for example in pregnancy, obesity (obesity hypoventilation syndrome).
- Airway obstruction/narrowing – for example in snorning, sleep apnea.
- Psychological – for example in night terrors, panic attacks.
Trouble Breathing in Pregnancy
Shortness of breath in pregnancy is a common symptom due to iron-deficiency anemia. Another common cause of breathing difficulties in late pregnancy may be due to reduced space for diaphragmatic contraction and lung expansion due to the presence of the enlarged uterus.
Trouble Breathing During, After Exercise
Almost every acute and chronic cause of dyspnea will result in breathing difficulties upon exertion and activity. Refer to Acute Causes of Dyspnea and Chronic Causes of Dyspnea.