Pictures of Insects that Feed on Humans and Cause Diseases
Bed Bugs
Bed bugs are tiny insects belonging to the Cimicid family of parasites. These bugs survive by feeding on the blood of mammals like humans. The most common of the bed bug species is Cimex lectularius which has a preference for human blood. These insects are commonly referred to as bed bugs as they tend to hide in mattresses, headboards and bed frames during the day. They emerge at night to feed on sleeping human hosts. The oval-shaped adult bed bug is about 4 to 5 millimeters long and up to 3 millimeters wide. It has a light brown to reddish brown color.
Bed bugs feed for between 3 to 10 minutes on a person. After fully feeding it becomes engorged and then retreats. Usually bed bugs live in close vicinity to humans but does not reside on the human body. Its bite and subsequent feeding causes red spots on the skin which are usually orientated in a line or clusters. The site of the bite is typically itchy. Bed bugs more often feed on the face, neck, arms and hands and to a lesser degree on the legs. It can feed at any site on the body and the location of the bite depends on where it can easily gain access and the warmth of the area.
Human Lice
Human lice are tiny wingless insects that infest different parts of the human body. There are three types of human lice which infests certain areas of the body. Pediculus humanus corporis is also known as body lice because it infests the human body. Pediculus humanus capitis infests the head and is therefore known as head lice while Pthirus pubis infests the pubic region and is known as pubic lice (crabs). Each type of lice is different despite belonging to the same species. Only body lice can spread diseases such as typhus or trench fever.
Lice feed on human blood up to 5 times a day, spending about 30 to 45 minutes feeding each time. The lice tends to cling on body hair between feeds. The typical symptoms are itching at the site of feeding along with skin rashes. Patients also report a tickling sensation when the lice move around on the body. Lice are easily spread from person to person through direct contact and pubic lice can be sexually transmitted. Lice are not necessarily associated with poor hygiene or poverty as it is often thought. The most common type, head lice, easily spreads among school children.
Mites
There are a number of different mites that can cause infestations in humans. The more common mites are the scabies, demodex and chiggers mites. Demodex and chiggers can cause intense symptoms but are usually not as serious or prevalent as scabies. House dust mite is by far the most widespread. It feeds off dead human skin cells and usually does not cause an infestation as such.
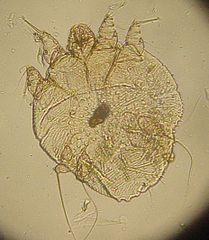
Scabies Mite
The Sarcoptes scabiei mite is the cause of scabies, an itchy skin disease. When the itch mite infests human skin, it burrows into the skin where it lives and lays eggs. This triggers an allergic reaction resulting in severe itching. These mites have four legs and are very tiny with females mites measuring up to 0.45 millimeters in length and 0.35 millimeters wide. Adult male mites are about half the size of females. Only about a dozen mites infest a person at any one time. These mites live for about 2 months with females laying about 2 to 3 eggs per day for most of their lifespan.
The scabies mite rapidly spreads among people in close contact particularly individuals living in crowded quarters and institutionalized patients. It is a not a matter of personal hygiene and affects any person from any socioeconomic group. Although humans may have a reaction when coming in contact with mites from pets, these mites are species-specific and animal scabies mites will not cause full-blown scabies in humans. Apart from the itchy skin which is typically worse at night. tiny burrow tracks may also be evident on the skin.
Ticks
Ticks are arthropods and may have between 6 to 8 legs depending on the stage of development. There are a number of different tick species that infests animals. All of these ticks may also feed on humans. Although humans are an accidental host, ticks can still cause very serious diseases in people. Ticks may be found on a number of different animals, both domestic and wild, and may spread to humans during close contact. It can also spread to humans through grass and foliage when the tick drops off the animal and attaches to people who pass by.
These insects thrive off mammalian blood and certain species of ticks have a preference for specific animals like dogs, rabbits, cattle, mice and deer. Some ticks will attach and feed off any mammal that it comes across while others will not readily feed on humans. Ticks may easily spread infectious diseases caused by a range of microbes including bacteria, viruses and protozoa. The symptoms of the tick bite can range from mild discomfort and itching, to severe allergic reactions at the site of the bite or even cause limp paralysis in the legs which spreads upwards and can eventually lead to death.
Common Tick-Borne Diseases
Apart from tick paralysis, most other diseases are caused by pathogens that are carried by ticks and transmitted to humans through tick bites. In the United States, these tick-borne illnesses include :
- Anaplasmosis
- Babesiosis
- Ehrlichiosis
- Lyme disease
- Rickettsia parkeri Rickettsiosis
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
- STARI (Southern Tick-Associated Rash Illness)
- Tickborne relapsing fever (TBRF)
- Tularemia
- 364D Rickettsiosis
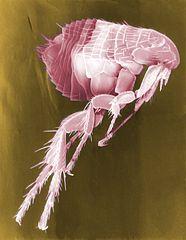
Fleas
There are a number of different fleas that have a preference for different species of mammals. Human fleas (Pulex irritans) do not live on humans but prefer to feed on people and pigs when the opportunity arises. However, this type of flea is usually not responsible for flea infestations in the home. It is the cat flea and sometimes the dog flea that more often causes home infestations. Despite the name, the cat flea and dog flea will readily feed on humans once they make contact and can infest a home that does not have pets. Fleas feed on the blood of mammals but can survive even in cold temperatures for up to 1 to 2 months without a blood feed.
Adult fleas are flattened tiny insects that have a remarkable ability to jump vast distances in respect to its size. The main symptoms of flea bites is an itchy skin rash as a result of a localized allergic reaction. Usually flea bites do not cause any serious disease and the flea quickly moves on after feeding. However, the intense itching and subsequent scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections. Sometimes fleas can transmit diseases such as murine typhus and the bubonic plague, although modern measures to control flea infestations have drastically reduced the incidence of these diseases.
Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes are types of flies that belong to the Nematocera family of flies. Although some types of mosquitoes are harmless, most feed on human and animal blood. The majority of these feeding mosquitoes do not cause disease but some species are known to carry viral or protozoal diseases. There are hundreds of species of mosquitoes but it is the Anopheles, Aedes and Culex species that are most likely to spread diseases. One of the widely known mosquito-borne diseases is malaria which kills about 1 million people throughout the world every year. Mosquitoes have a very short lifespan but reproduce so rapidly that it causes infestations in certain areas.
The adult mosquito is rarely longer than 16 millimeters although the size can vary from one species to another. They are able to fly and can easily travel distances to find the ideal living environment with sufficient hosts to feed upon. An elongated proboscis at the front of the head of the mosquito pierces human skin and allows the insect to feed on blood. Saliva released by the mosquito can cause intense itching at the site of the feeding but may also transmit viruses and protozoa into the host.
Flies
Flies are common insects present throughout the world. Most of us know the housefly which can sometimes cause diseases such as typhoid and dysentery by contaminating the food that people eat. However, it is the biting flies that are more likely to cause diseases. Some of these flies feed on human blood but in the process transmit pathogens similar to the way mosquitoes spread disease. There are thousands of species of flies and the size and other physical features vary greatly apart. These two-winged insects can travel great distances and hide in different modes of transport thereby allowing it to move across countries and even continents.
Two species of blood-sucking flies that are known to cause serious disease is the tsetse fly and the sandfly. The tsetse fly may transmit the protozoan Trypanosoma brucei which causes African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness). Sandflies may transmit the Leishmania protozoan which causes the disease leishmaniasis or Bartonella bacilliformis bacteria resulting in bartonellosis. These diseases are not usually seen in the mainland United States but travelers to endemic regions need to be aware of the dangers as flies are often thought to be harmless insects.