Mouth Pain (Sore Mouth) and Throat Pain When Swallowing
What is stomatodynia?
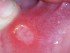
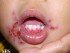
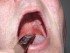
Stomatodynia is the medical term for pain in the mouth. This can include pain or discomfort of the lips, tongue (glossodynia), palate and/or inner lining of the mouth cavity known as the buccal mucosa. Often dental pain, involving the teeth and/or gums may be described as mouth pain.
A chronic type of mouth pain that may occur in episodes and last for years is known as burning mouth syndrome. It can be quite severe in nature and often the sensation is similar to scalding the mouth i.e. burning the mouth when ingesting very hot food or drink. There may also be other sensory changes like numbness or tingling of the lips or tongue, sensation of a dry mouth, and changes in taste. This condition has a host of causes, some of which are mentioned below. However, it should be assessed and treated as a syndrome on its own.
Causes of a Painful Mouth
With the growing incidence of oral cavity cancer, a malignancy should not be ruled out as a possible cause especially if the risk factors are present – family history, alcohol abuse, cigarette smoking, tobacco chewing and areca nut-betel leaf chewing. Hormonal change, particularly in women, and nerve damage is more likely to result in burning mouth syndrome.
Common Causes of Mouth Pain
- Aphthous stomatitis (recurrent mouth sores)
- Dental abscess, tooth cavity, gingivitis, dental hypersensitivity (sensitive teeth)
- Trauma from teeth, poorly fitting dental implants, dentures
- Snoring – many people who snore report mouth pain upon waking as result of mouth dryness and increased air pressure while sleeping
- Idiopathic (unknown)
Most cases of mouth pain are due to mouth sores (aphthous ulcers), dental pain, trauma or of unknown origin (idiopathic). Mouth pain may occur in conditions that cause a dry mouth, like diabetes, Sjogren’s syndrome and the use of certain of drugs. In these cases, mouth pain is common and may be associated with the dryness, in addition to the susceptibility of the mouth lining to infections and trauma from daily activities like eating.
Infectious Causes of Mouth Pain
- Oral candidiasis
- Coxsackie A virus
- Herpes simplex virus
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) – hairy leukoplakia
Nutritional Deficiencies
Mouth pain due to nutritional deficiencies are not uncommon but are often missed if other signs and symptoms are not evident. The following deficiencies may result in mouth pain :
- Iron
- Folate
- Vitamin B12
Chemical Causes of Mouth Pain
- Severe gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
- Persistent vomiting as seen with in hyperemesis gravidarum in pregnancy or in eating disorders like bulimia
- Alcohol abuse *
- Tobacco chewing *,**
- Cigarette smoking *, **
- Areca nut and betel leaf **
- Ingestion of corrosive substance like detergents (strong acids or lyes), concentrated alcohol (home made brews)
- Prescription drugs like sulfonamides
- Narcotics – crack cocaine, crystal meth
* Cigarette smoking, tobacco chewing may be associated with leukoplakia.
** Cigarette smoking, tobacco chewing and areca nut and betel leaf chewing may be associated with oral cancer.
Dental pathology may often be evident with most of the chemical causes including tooth cavities, discoloration of the teeth, brittle teeth and receding gums.
Diseases Causing Mouth Pain
Some of these systemic conditions may cause mouth pain although the primary pathology may be isolated to other sites of the body.
- Bechet’s syndrome
- Celiac disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease – Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis
- Leukopenia
- Reactive arthritis (previously Reiter’s syndrome)
Skin Diseases Causing Mouth Pain
The following conditions may involve the mouth.
- Erythema multiforme
- Lichen planus
- Pemphigus vulgaris
Throat Pain When Swallowing
Swallowing is reflex that is largely involuntary. Only the first stage of swallowing, known as oral swallowing is under voluntary control, where the tongue pushes the chewed food to the back of the throat. The swallowing process then continues with pharyngeal and esophageal swallowing.
Normally, swallowing should be neither difficult nor painful. Swallowing hard and partially chewed foods could cause some difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) and even painful swallowing (odynophagia). However, pain when swallowing thoroughly chewed foods and drinks is almost always a sign of pathology within the mouth, throat or esophagus (gullet). This may be acute, as is often seen with infections, or chronic (persistent, long term).
Throat pain when swallowing may also be accompanied by other symptoms :
- difficulty swallowing
- coughing
- regurgitation
- gagging
- mouth pain
- chest pain
- hoarse voice
Some of these symptoms may be unrelated to the act of swallowing but rather a consequence of the causative condition. Bleeding after swallowing is a serious sign and warrants immediate medical attention. Refer to blood in the mouth.
Causes of Throat Pain When Swallowing
Throat pain when swallowing indicates pathology in the throat (pharynx) and may include the distal part of the mouth and proximal part of the esophagus. Most cases of throat pain when swallowing is a result of pharyngitis – inflammation of the throat that typically presents as a sore throat. The causes of these conditions are discussed further under :
Infections
- Tonsillitis (tonsils)
- Pharyngitis (pharynx)
- Stomatitis (mouth)
- Esophagitis (esophagus)
Most cases are due to bacterial (refer to strep throat) or viral infections. Fungal infections are less common and are more likely to be seen in immunocompromised patients, like with poorly managed diabetes mellitus and HIV infection.
Trauma
Trauma to the mouth, throat and upper esophagus due to the causes below may cause throat pain when swallowing.
- Mechanical
- Snoring
- Post-operative (throat surgery like a tonsillectomy)
- After diagnostic procedures like a laryngoscopy/endoscopy
- Tonsil stones
- Foreign bodies
- Mouth breathing
- Voice strain
- Radiation
- Chemical
- Acid reflux
- Air pollution
- Alcohol abuse
- Corrosive substances
- Smoking – tobacco (cigarettes, cigars), narcotics
- Chewing tobacco, areca nut/betel leaf
- Repeated vomiting (gastric acid) – pregnancy, eating disorders and other usually chronic gastrointestinal diseases
Mouth Conditions
- Mouth sores and ulcers – aphthous stomatitis
- Skin conditions – lichen planus, pemphigus vulgaris, erythema multiforme
- Nutritional deficiencies – iron, folate, vitamin B12
- Dental conditions – tooth cavity, abscess, gingivitis, periodontitis
- Sjogren’s syndrome
Esophagus Conditions
- Achalasia
- Esophageal spasms – diffuse or nutcracker syndrome
- Esophageal tears/perforation
- Esophageal ulcers
- Esophageal webs
- GERD
- Zenker’s diverticulum
Cancer
- Throat cancer
- Mouth (oral cavity) cancer
- Nose (nasal cavity) cancer
- Esophageal cancer
Other Diseases
- Bechet’s syndrome
- Celiac disease
- Inflammatory bowel disease – Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis
- Leukopenia
- Reactive arthritis (previously Reiter’s syndrome)