Tightness in the Abdomen – Causes of Tight Stomach Feeling
There are a number of different sensations that a person may experience which does not always correlate with specific medical symptoms. Broadly abdominal discomfort is the term for all abdominal sensations that are technically not abdominal pain. Other common sensations like abdominal cramps and even abdominal tenderness are related to abdominal pain.
Tight Feeling in the Abdomen
Another term, abdominal tightness or tightness within the abdomen, is a type of abdominal discomfort associated with firmness or fullness in the abdomen – whether actual physical firming present or simply a tight sensation. The abdominal cavity is the largest cavity in the body and contains the most of amount of organ. Tightness may emanate from the abdominal wall or organs and structures within the abdomen (intra-abdominal).
It is a non-specific symptom which does not clearly indicate the exact cause unless it is associated with other symptoms. Sometimes the sensation of tightness in the abdomen is generalized meaning that it can be felt throughout the abdomen and is difficult to localize. At other times the sensation may emanate from certain regions of the abdomen.

Symptoms with Abdominal Tightness
Abdominal tightness or a tight feeling in the abdomen is a symptom and not a disease. It may or may not be accompanied by other symptoms. Since the abdominal cavity has mainly the organs of digestive system, the other symptoms that accompany abdominal tightness more commonly includes :
- Nausea with or without vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal distention – enlargement
- Stomach bloating – sensation of fullness
- Heartburn
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Excessive belching
- Excessive flatulence
- Loss of appetite
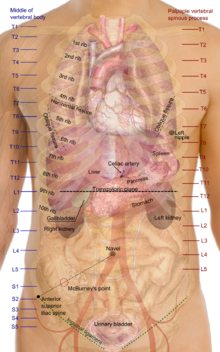
Location of Abdominal Tightness
At times the sensation of abdominal tightness is localized to specific regions in the abdomen. This may help isolate the cause to certain organs although many organs may extend from one quadrant to another.
- Right upper quadrant (RUQ) : liver, gallbladder, right kidney, pancreas, colon, small intestine. These organs may cause upper right abdominal pain.
- Left upper quadrant (LUQ) : stomach, spleen, pancreas, colon, small intestine, left kidney. These organs may cause upper left abdominal pain.
- Right lower quadrant (RLQ) : right ureter, colon, small intestine, right ovary and fallopian tube. These organs may cause lower right abdominal pain.
- Left lower quadrant (LLQ) : left ureter, colon, small intestine, left ovary and fallopian tube. These organs may cause lower left abdominal pain.
The small intestines primarily occupy the middle of the abdomen. The abdominal portion of the aorta also runs down the middle of the abdomen. The lower middle part of the abdomen is occupied by the uterus, bladder and prostate.
Causes of Abdominal Tightness
Some of the more likely causes of a tight feeling in the abdomen has been discussed below. This often overlaps with other sensations in the abdomen, such as abdominal bloating.
Injury and Strain
- Abdominal injury may sometimes be mild so as not to cause pain. A person may instead experiences tightness at the site of injury and tenderness may also be present. The tight sensation can emanate from the abdominal wall and in particular the muscle as may been with muscle bruising and cramps. Alternatively the inner organs may be injured and be the site of the tightness.
- Abdominal muscle cramps may arise with strenuous physical activity involving the use of these muscles or with abdominal exercises. It is more likely to occur in a person who is not physically fit and apart from the cramps, the other parts of the muscles may feel tight. Tightness also arises with compression of the intra-abdominal contents.
- Peritonitis is the inflammation of the peritoneum, the lining of the abdominal cavity. It typically causes intense abdominal pain although abdominal tightness may also be present at the same time. Sometimes tightness may be the early symptoms and is typically isolated to the affected part of the peritoneum.
Fluid and Growths
- Ascites is accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity. Although it can lead to pain in severe cases, there is no symptoms in the early stages. Eventually as the condition worsens and the abdomen distends, there may be a feeling of compression or tightness. The sensation of abdominal tightness is usually generalized.
- Mass within the abdomen can be a tumor (malignant or benign), abscess or cyst. An intra-abdominal abscess tends to be painful on its own. Other masses can be painful when it extensively damages tissue to compresses on nerves. Malignant tumors (cancer) invades healthy tissue and can eventually become painful.
Digestive Organs
- Constipation and diarrhea are symptoms and not diseases on its own. It may be accompanied by other symptoms such as abdominal tightness. With constipation this could be attributed to excessive straining during a bowel movement or the accumulation of feces in the colon. Diarrhea may also be accompanied by tight feeling in the abdomen which could be due to intestinal cramps, bowel tenesmus (urging) and excessive gas.
- Fecal impaction where stool becomes compacted and obstructs the rectum and colon. It is a complication of severe constipation.
- Gastritis is inflammation of the stomach wall that typically presents with a dull gnawing ache often describes as soreness. It can be a painful condition when there is an acute exacerbation or ulcers. the tightness is felt just under the left ribcage and can extend to the upper middle abdominal region.
- Hiatal hernia where a portion of the stomach protrudes into the thoracic (chest) cavity. It is usually not a painful condition except in certain instances. However, a tight uncomfortable feeling in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen is typically reported. This is felt under the left ribcage.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is an abnormality with bowel habit accompanied by abdominal discomfort or pain. Sensations such as abdominal tightness are common and may be present even when the bowel habits are normal. It may also be accompanied by abdominal distention known as functional bloating.
- Obstruction within the gastrointestinal tract, from the stomach to the colon, can contribute to a feeling of tightness especially when it impedes the movement of the gut contents like food and waste.
Urinary
Urinary tract infections, particularly when it involves the bladder, ureters or even the kidneys. A burning pain is often present but tightness may persist throughout the condition along with the pain. Cystitis (bladder inflammation) is located at the bottom central part of the abdomen, the two ureters on either side are located approximately in line with the flanks and the kidneys are tucked towards the back in the upper part of the abdomen.
Male and Female
- Gynecological problems in women such as uterine fibroids, uterine polyps, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) and pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Menstrual cycle tightness may be normal just before and during ovulation or menstruation. In premenstrual syndrome (PMS), tightness may accompany other symptoms such as mood swings prior to menstruation.
- Pregnancy may cause lower abdominal tightness especially as the fetus grows. This may be caused by compression of the abdominal organs or stretching of the abdominal wall.
- Prostate enlargement, inflammation or cancer may cause a tight sensation in the lower abdomen of men.
References:
- Tight stomach. Medical News Today
Reviewed and updated on August 13, 2018.